Chan, K. S. L.; Wasa, M.; Chu, L.; Laforteza, B. N.; Miura, M.; Yu, J.-Q. Nat. Chem 2014, advance online publication
DOI: 10.1038/nchem.1836
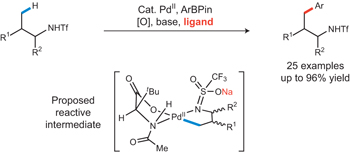
There have been numerous developments in C–H activation reactions in the past decade. Attracted by the ability to functionalize molecules directly at ostensibly unreactive C–H bonds, chemists have discovered reaction conditions that enable reactions of C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds with a variety of coupling partners. Despite these advances, the development of suitable ligands that enable catalytic C(sp3)–H bond functionalization remains a significant challenge. Herein we report the discovery of a mono-N-protected amino acid ligand that enables Pd(II)-catalysed coupling of γ-C(sp3)–H bonds in triflyl-protected amines with arylboron reagents. Remarkably, no background reaction was observed in the absence of ligand. A variety of amine substrates and arylboron reagents were cross-coupled using this method. Arylation of optically active substrates derived from amino acids also provides a potential route for preparing non-proteinogenic amino acids.
Professor Jin-quan Yu, the Scripps research institute, work on the discovery of catalytic carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bond forming reactions based on C-H activation.
In the past decade, palladium-catalyzed CH activation/CC bond-forming reactions have emerged as promising new catalytic transformations. However, development in this field is still at an early stage compared to the state of the art in cross-coupling reactions using aryl and alkyl halides. Therefore, the development of suitable ligands that enable catalytic C–H bond functionalization remains a significant challenge. Recently, the use of inert C–H bonds as coupling partners for Suzuki coupling with organoboron reagents has been made possible using Pd(II)/Pd(0) catalysis.[1,2,3]
This time, Yu and coworkers have developed Pd(II)-catalysed cross-coupling of g-C(sp3)–H bonds in R–NHTf with arylboron reagents using MPAA (mono-N-protected amino acid) ligand.
- Rekated links
The Yu lab
- Related papers
[1] “Palladium-catalyzed alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C–H bonds with methylboroxine and alkylboronic acids: two distinct C–H activation pathways ”
Chen, X.; Goodhue, C. E.; Yu, J-Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12634. DOI: 10.1021/ja0646747
Palladium-catalyzed alkylations of sp2 and sp3 C−H bonds with either methylboroxine or alkylboronic acids were developed. Ag2O or AgCO3 is used as a crucial oxidant and promoter for the transmetalation step. Ether, ester, alcohol, and alkene functional groups are tolerated. A new C−H activation pathway differing from the cyclometalation process is elucidated using methylboroxine as the coupling partner.
[2] “Palladium(II)-catalyzed C–H activation/C–C cross-coupling reactions: versatility and practicality. ”
Chen, X.; Engle, K. M.; Wang, D-H.; Yu, J-Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5094. DOI: 10.1002/anie.200806273
In the past decade, palladium-catalyzed C–H activation/C–C bond-forming reactions have emerged as promising new catalytic transformations; however, development in this field is still at an early stage compared to the state of the art in cross-coupling reactions using aryl and alkyl halides. This Review begins with a brief introduction of four extensively investigated modes of catalysis for forming C![[BOND]](https://en.chem-station.com/wp-content/plugins/lazy-load/images/1x1.trans.gif) C bonds from C
C bonds from C![[BOND]](https://en.chem-station.com/wp-content/plugins/lazy-load/images/1x1.trans.gif) H bonds: PdII/Pd0, PdII/PdIV, Pd0/PdII/PdIV, and Pd0/PdII catalysis. A more detailed discussion is then directed towards the recent development of palladium(II)-catalyzed coupling of C
H bonds: PdII/Pd0, PdII/PdIV, Pd0/PdII/PdIV, and Pd0/PdII catalysis. A more detailed discussion is then directed towards the recent development of palladium(II)-catalyzed coupling of C![[BOND]](https://en.chem-station.com/wp-content/plugins/lazy-load/images/1x1.trans.gif) H bonds with organometallic reagents through a PdII/Pd0 catalytic cycle. Despite the progress made to date, improving the versatility and practicality of this new reaction remains a tremendous challenge.
H bonds with organometallic reagents through a PdII/Pd0 catalytic cycle. Despite the progress made to date, improving the versatility and practicality of this new reaction remains a tremendous challenge.
[3] “Aromatic C–H coupling with hindered arylboronic acids by Pd/Fe dual catalysts”
Yamaguchi, K.; Kondo, H.; Yamaguchi, J.; Itami, K. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3753. DOI:10.1039/c3sc51206a
An aerobic oxidative coupling of arenes/alkenes with arylboronic acids (C–H/C–B coupling) using catalytic Pd(II)–sulfoxide–oxazoline (sox) ligand and iron–phthalocyanine (FePc) has been developed. This dual catalyst system enables the synthesis of sterically hindered heterobiaryls and styrene derivatives under air without stoichiometric co-oxidants. Additionally, this chemistry demonstrated an advance toward an enantioselective biaryl coupling through C–H functionalization.
- Related Books