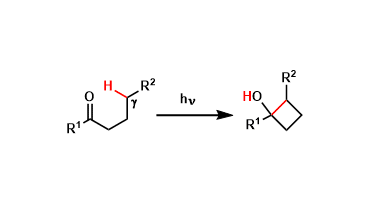
General Characteristics In the Norrish-Yang reaction, the C-H bond at the γ-position of ketones is homolytically cleaved by photo-irradiation and the ensuing rearrangement leads to the formation of ...
Monthly Archives: February 2016
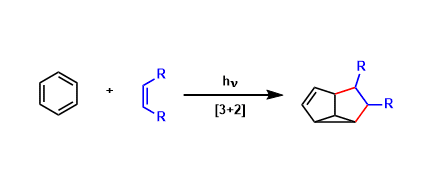
Aromatic Meta Photocycloaddition
General Characteristics Aromatic rings and alkenes undergo [3+2] cycloaddition under photo-irradiated conditions. This reaction provides complex fused ring skeletons that are otherwise difficult to ...
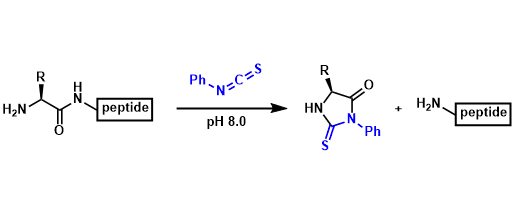
Edman Degradation
General Characteristics The Edman degradation is a way to determine the primary structure of peptides. Phenyl isocyanate reacts with the N-terminus amino acid residue and only that residue is cleaved ...
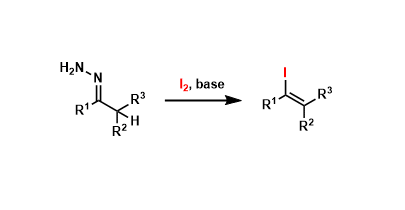
Barton Vinyl Iodide Synthesis
General Characteristics Hydrazones can be converted into vinyl iodides using molecular iodine under mild conditions. Vinyl selenides can be synthesized as well in similar manner using reagents such ...
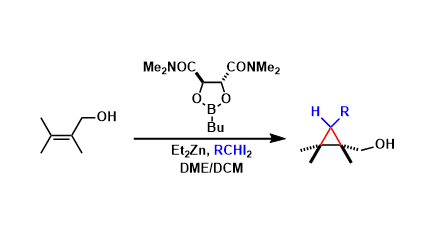
Charette Asymmetric Cyclopropanation
General Characteristics The Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation can be rendered asymmetric by using the chiral boronic acid ester as a reagent. An allylic hydroxyl group is needed in substrates as a ...
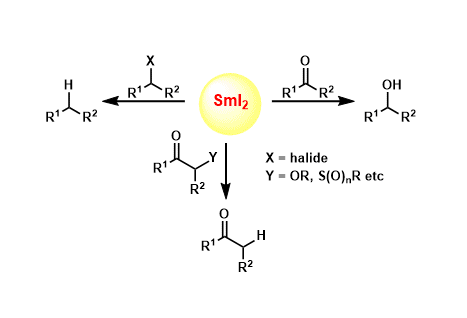
Samarium(II) Iodide
General Characteristics Samarium(II) iodide (SmI2) is a mild one-electron reducing agent used for various reductive reactions of carbonyl compounds, organic halides, and electron deficient olefins. ...
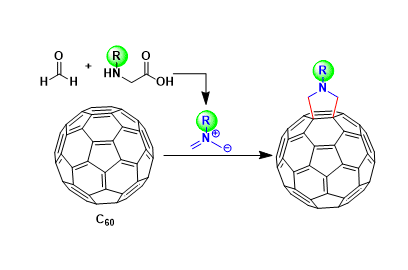
Prato Reaction
General Characteristics The derivatization of fullerenes using azomethine ylides via 1,3-dipoloar cycloaddition was developed by Prato. This methodology is applicable to carbon nanotubes as well. ...